使用原始设备制造商 (OEM) 自定义输入,可以为新的非标准 Android 功能添加新的汽车输入事件。现有的 Android KeyEvent 不会映射非标准输入事件,前者是通用的,适用于所有 Android surface,但无法扩展用于实现 OEM 专用功能。例如,位于方向盘控件上的按钮,按下此按钮,系统便会打开包含汽车当前位置信息的地图应用(通过 intent)。借助此功能,驾驶员在驾驶过程中可以直观地了解其当前位置,而不会分心。
本文介绍了如何重复使用现有 Android KeyEvent 来创建 CustomInputEvent,以便仅在无法使用任何 Android KeyEvent 代表相应功能时使用。
HW_CUSTOM_INPUT
OEM 自定义输入由 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 和 CustomInputEvent.java 代表。HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 是由汽车硬件(车载 HAL)实例化的原生事件。OEM 确定如何实例化此事件。对 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 的访问权限已设为 [read only],即 VehiclePropertyAccess:READ。
为了确保车载 HAL 始终能够广播最新的可用值,请将 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 通知设置为 ON_CHANGE,即 VehiclePropertyChangeMode:ON_CHANGE。
HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 值由一组通用 int32 组成,已设为 global。三个通用整数为:
第一个元素代表将由 OEM 定义的输入代码。您可以将任何语义与输入代码相关联。
第二个元素用于存储目标屏幕,例如主屏幕或仪表盘。
第三个元素包含事件的重复次数。例如,用于指示按下按钮的次数。
CustomInputEvent 和 Car Input API
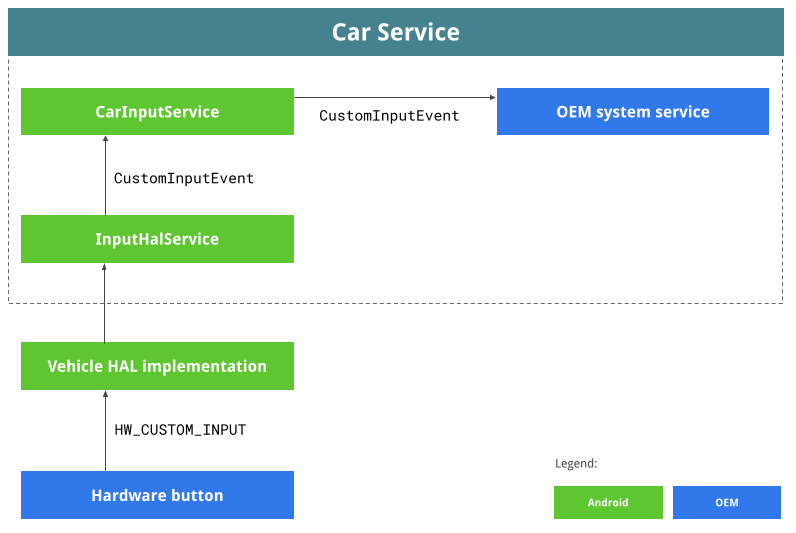
InputHalService 是从车载 HAL 接收传入 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 的汽车服务。
InputHalService 将传入的 HW_CUSTOM_INPUT 转换为 CustomInputEvent,后者是一种 Java Parcelable 类,与相应 aidl 接口一起位于 car-lib/src/android/car/input。
CarInputService 是一项核心汽车输入服务,用于接收传入的 CustomInputEvent,然后将其发送到任何已注册的 Android 系统服务。
如需注册和接收传入的 CustomInputEvent,系统服务必须:
通过 CarInputManager#requestInputEventCapture 进行注册,并传递
CarInputManager.INPUT_TYPE_CUSTOM_INPUT_EVENT作为输入类型参数。如需取消注册,服务必须调用 CarInputManager#releaseInputEventCapture。
下图展示了 OEM 自定义输入事件的工作流程。
OEM Android 系统服务
OEM 提供自己的 Android 系统服务,用于处理从 CarInputService 传入的 CustomInputEvent。
只有那些标有 android.permission.INJECT_EVENTS 特许权限的服务才能通过 Car Input API (CarInputManager) 注册并接收 CustomInputEvent。任何第三方服务或应用均无法通过此 Android 系统权限签名(仅限 OEM 服务)。因此,任何第三方服务或应用均无法向 Car Input API 进行注册。
OEM Android 系统服务可以访问 SystemApi 和公共方法。
参考实现
如需了解相关示例和指南,请参阅 packages/services/Car/tests/SampleCustomInputService 中的参考实现。例如,在方向盘控件中添加新按钮。按下后,此新按钮会启动包含当前汽车位置信息的地图应用。
在此示例中,OEM 选择以 INPUT_CODE_F1(第一个 CustomInputEvent 便捷函数)来代表这项新功能(打开包含当前汽车位置信息的地图应用)。
在启动过程中,此服务会通过 requestInputEventCapture 向 CarInputManager 注册自身(请参阅参考实现注册代码)。
收到传入的 CustomInputEvent 时,此服务会发送 intent 以启动地图应用。如需了解这是如何实现的,请参阅 CustomInputEventListener.java。
