新一代车辆将支持多个屏幕,其中一些屏幕可通过 Android 平台进行操作,以提供丰富的内容。本页面介绍了将仪表板和其他屏幕集成到 Android Automotive IVI 系统中的关键元素。
Android 中的外部屏幕
Android 10 使用 android.app.Presentation API 来支持使用外部屏幕。presentation 是一种独特的对话框,用于在辅助屏幕上呈现内容。presentation 在创建时与目标 Display 相关联,并根据屏幕指标配置其上下文和资源配置。
仪表板屏幕
Presentation API 足以支持典型的仪表板屏幕,允许以下内容:

Presentation API 不需要:
- 单独的音频焦点。
- 运行整个 activity 或应用。
- 考虑并发用户输入。
- 处理触摸事件。
如需详细了解如何使用多个屏幕,请参阅多屏幕概览。
前提条件:对 Android WindowManager 的过往开发有一定了解会对您有所帮助。
支持的内容类型
有些车辆可能不希望 Android 直接绘制仪表板图形,但仍希望显示精细导航或音乐标题等信息。Android 可以通过多种方式发送此类数据。Android 设备可以通过以下方式发送仪表板内容:
- 基于元数据,例如通过
CarVendorExtensionManager或VehicleNetworkService经由 CAN 发送消息。仪表板系统必须基于元数据创建合适的图形。 - 基于图形,向物理或虚拟屏幕发送。屏幕可以是仪表盘中的专用屏幕,也可以是全图形仪表板屏幕的一部分。
基于图形的仪表板屏幕的硬件架构示例:
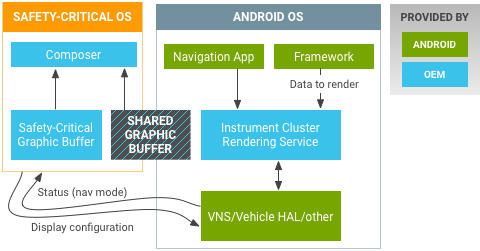
图 2. Android Automotive 基于图形的仪表板屏幕示例。
安全关键型操作系统(负责渲染仪表板)和 Android 操作系统可以位于同一多核 SoC(例如,适用于实时操作系统的专用 Cortex-R 和适用于 Android 的 Cortex-A)中。接口可以是以太网 AVB(音视频桥)、LVDS 或 HDMI。在 Android 中,图形仪表板可以作为虚拟屏幕连接,从而在屏幕 HAL 实现后隐藏硬件架构。
后座限制
对于后座娱乐内容,Presentation API 具有以下限制:
- 无法投影整个 activity(presentation 只是一个对话框)。
- 只有一个可用的音频焦点。
- 没有并发用户。
- 没有针对外部屏幕的直接触摸事件(需要单独的注入流)。
