根据 Android 兼容性定义文档的规定,原始设备制造商 (OEM) 必须提供一种支持应用开发的方式。不过,如果在汽车内提供与移动设备类似的开发者选项,会导致汽车容易受到攻击。现在,OEM 可以使用经过身份验证的加密令牌机制控制开发者选项。具体来说,OEM 可以:
- 设置首次启动之前所需的默认限制。
- 如果愿意,可以使用加密令牌安全地向开发者授权。
- 在开发者通过身份验证并获得授权后,应用限制更改。
本文介绍了一项参考实现,其中包括 Debugging Restriction Controller 应用和远程 Token Issuer 端点。
术语
除术语部分的术语外,本文还使用了以下术语:
- JSON Web Signature (JWS),在 RFC 7515 中有定义
- 美国国家标准与技术研究院 (NIST)
设计
OEM 可以使用 JSON Web Signature (JWS) 令牌 (RFC7515) 为开发者授权。在参考实现中,访问令牌由 OEM 颁发,并由 Restriction Controller 应用使用。访问令牌旨在抵御重放攻击和防范伪造令牌。
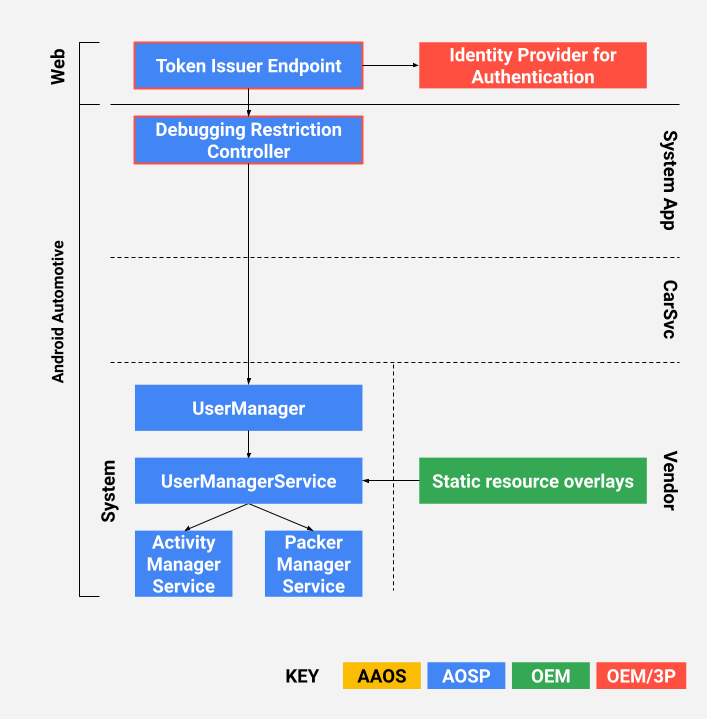
图 1. 设计
集成和配置
OEM 必须指定首次启动时所需的默认限制。为此,需要使用多个静态资源叠加层,以便替换 AOSP 框架中的默认值。
无头系统用户的默认限制可以使用 frameworks/base/core/res/res/values/config.xml 中的 config_defaultFirstUserRestrictions 字符串进行配置,例如:
<!-- User restrictions set when the first user is created.
Note: Also update appropriate overlay files. -->
<string-array translatable="false" name="config_defaultFirstUserRestrictions">
<item>no_debugging_features</item>
</string-array>您可以在 frameworks/base/core/res/res/xml/config_user_types.xml 中配置司机、乘客和访客的默认限制。OEM 可以叠加这些字符串,以便针对每种类型的用户分别设置默认限制,例如:
<user-types> <full-type name="android.os.usertype.full.SECONDARY" > <default-restrictions no_debugging_features="true"/> </full-type> <full-type name="android.os.usertype.full.GUEST" > <default-restrictions no_debugging_features="true"/> </full-type> </user-types>
AOSP 中的以下位置提供了一项参考实现:
packages/apps/Car/DebuggingRestrictionController
测试
Google 建议 OEM 从参考实现着手进行构建。
- 在叠加层文件中配置所需的限制后,编译 AAOS 并验证定义的流程。使用参考应用和支持本地 JWS 的服务来验证您的访问权限设置。
- 将系统配置为使用支持 JWS 的云服务(可选)。验证您是否在后端服务中遵守所需的流程。
