Media provides a platform on which to build media apps that provide safe, seamless, and connected infotainment experiences in every Android-enabled car. Media is an Android system application designed to provide a Distraction Optimized (DO) playback and browse experience for media apps. A fully functional implementation of Media is included with Android Open Source Project (AOSP).
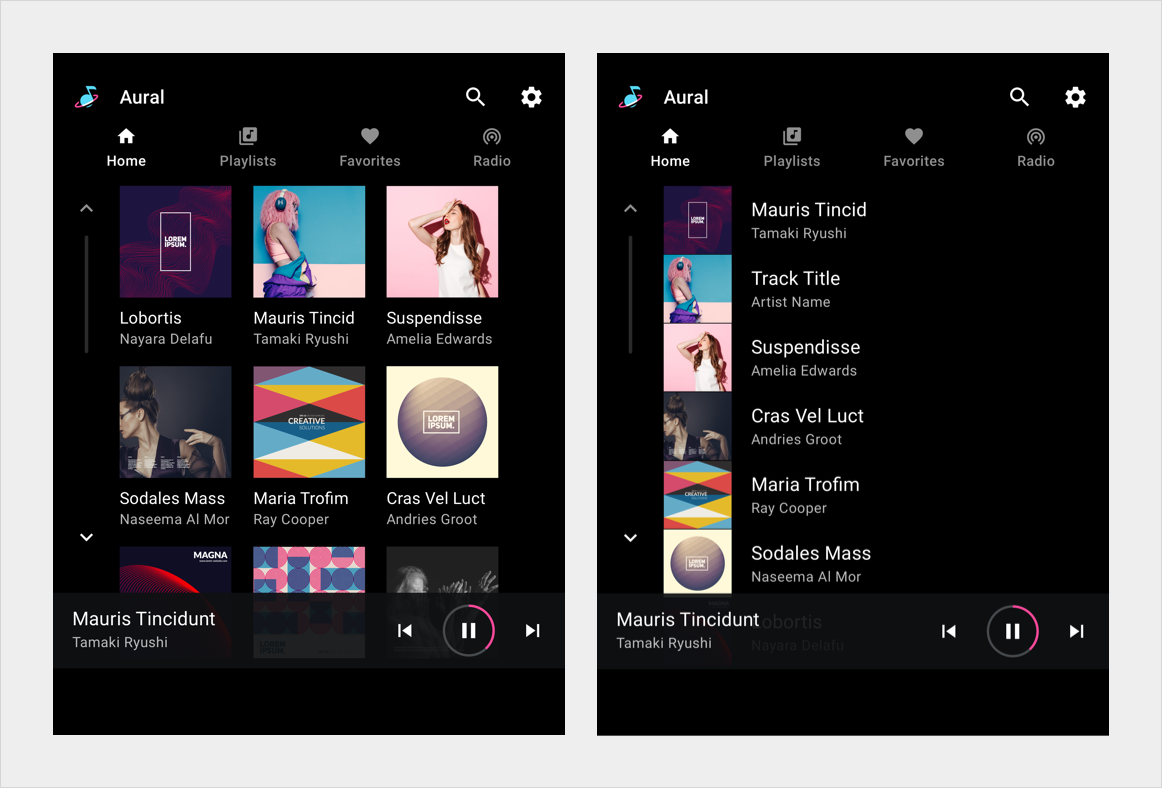
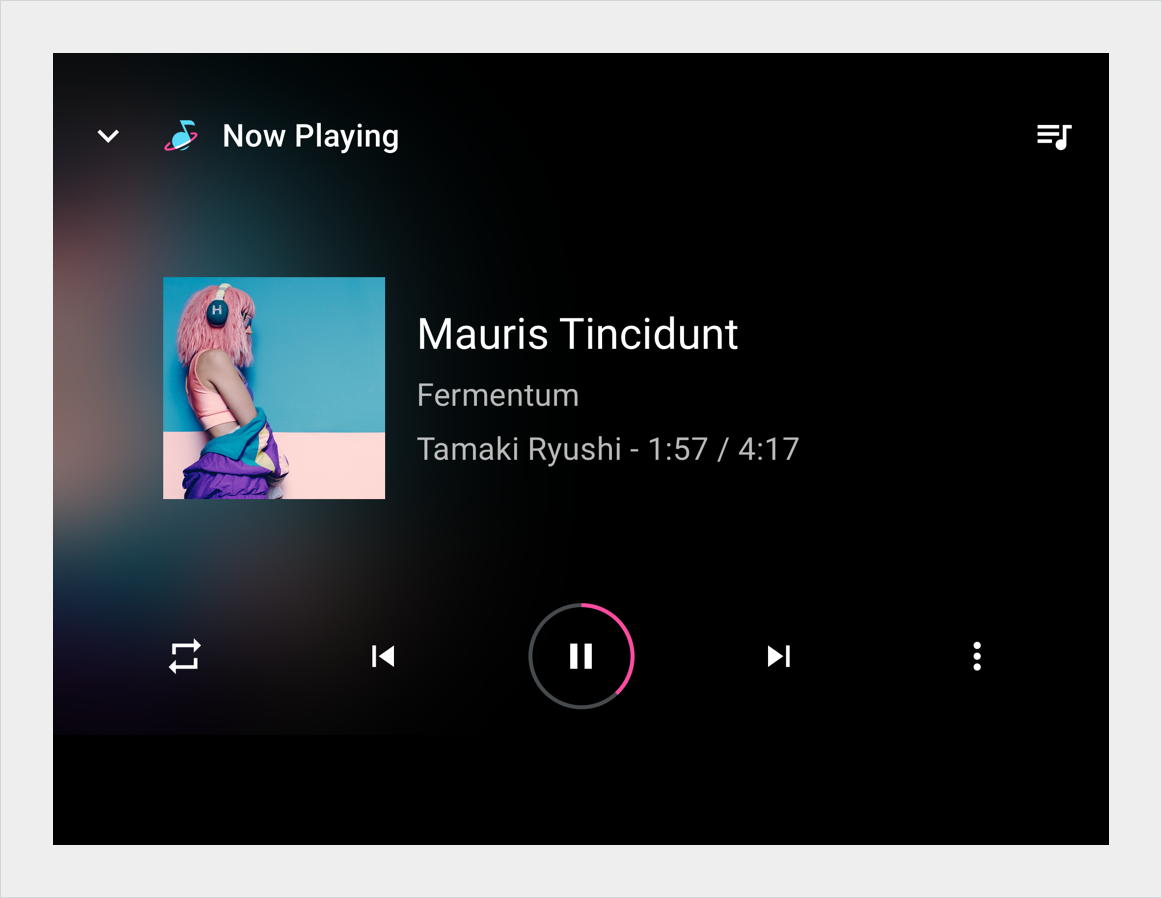
Figure 1. Media screen sample implementations.
To learn about Media, see the following pages:
- System components and user flows. Learn more about the components that interact with Media, as well as the most common user flows.
- Implement radio with media. Read how to integrate the Radio UI with Media to provide enable users to interact with media sources and radio as if they were a single application.
- Customize media. Learn how to work with styles and assets defined at different levels in the AOSP structure.
- Implement a media card. Implement a media card to display media metadata such as titles, album art, and more. A media card can also display a queue of media items, such as a playlist.
Terminology
These terms are used in this section.
- Playable Media items. Audio segments that can be played by the system such as songs, chapters of books, and episodes of podcasts
- Browsable Media items. Organizational elements used to group playable or other browseable media items such as song categories, a recent songs folder, as well as podcasts and playable media items sorted by artist, author, or audience.
Media features
Media provides these features.
| While driving | While parked |
|---|---|
|
Playback control.
Catalog browse.
|
Everything listed under While Driving as well as:
|
Tasks
This table describes the tasks of each party.
| Vehicle makers (vOEMs) | App developers | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Customization guidelines
The Media implementation included in AOSP uses Car UI Library to enable customization and provides a base theme and structure that can be adopted as is or modified according to the following restrictions. The following table describes OEM responsibilities regarding Media customization.
| Media customization | Description |
|---|---|
| SHOULD | Adjust overall theme and styling, including color pallette and sizing. |
| MAY | Modify the high-level structure of Media (for example, tab placement). |
MUST NOT |
Modify Media API contracts, including app branding:
Modify information architecture of:
|
