Android 10 支持使用 Android 构建系统来构建 odm 分区。
ODM 分区简介
原始设计制造商 (ODM) 能够为其特定设备(开发板)自定义系统芯片 (SoC) 供应商板级支持包 (BSP)。通过这样的方式,他们可为板级组件、板级守护程序或者其基于硬件抽象层 (HAL) 的自有功能实现内核模块,还可以替换或自定义 SoC 组件。
在较低的 Android 版本中,对于使用相同 SoC(或使用同一系列中的不同 SoC)的多款设备,此类自定义会导致设备无法使用同一个供应商映像。在 Android 10 及更高版本中,您可为自定义设置使用单独的 odm 分区,因而可为多个硬件 SKU 使用同一个供应商映像。
使用 product 分区和 ODM 分区
Android 9 开始支持构建 product 分区,让您可为不同 product.img 映像提供的多个软件 SKU 使用同一个系统映像。product 分区适用于软件 SKU,而 odm 分区适用于硬件 SKU。
有了专用的 product 分区和 ODM 分区,您可以使用 system 分区来容纳通用代码(这类代码在许多软件 SKU 之间共享),并使用 vendor 分区来容纳 SoC 专属 BSP 代码(这类代码根据特定的 SoC 在多款设备之间共享)。
使用单独的分区存在一定弊端,例如,磁盘空间管理难度更高(您必须预留一定的空间以满足未来的空间需求增长)。但是,Android 10 对动态分区的支持解决了磁盘空间问题,并且让您可以在无线下载 (OTA) 更新期间对设备进行重新分区。
ODM 组件
odm 分区包含以下 ODM 专用组件(类似于 vendor 分区),如下表所示。
| ODM 专用组件 | 位置 |
|---|---|
| 可加载内核模块 (LKM) | /odm/lib/modules/*.ko |
| 原生库 | /odm/lib[64] |
| HAL | /odm/lib[64]/hw |
| SEPolicy | /odm/etc/selinux |
| VINTF 对象数据 | /odm/etc/vintf |
init.rc 文件 |
/odm/etc/init |
| 系统属性 | /odm/build.prop |
| 运行时资源叠加层 (RRO) | /odm/overlay/*.apk |
| 应用 | /odm/app/*.apk |
| 特权应用 | /odm/priv-app/*.apk |
| Java 库 | /odm/framework/*.jar |
| Android 框架系统配置 | /odm/etc/sysconfig/* 和 /odm/etc/permissions/* |
不得使用自定义映像
请勿使用自定义映像,因为它们缺乏对以下方面的支持:
- 将模块安装到特定目标分区中。自定义映像支持将工件复制到映像中,但无法通过在构建规则中指定目标分区,将模块安装到特定分区中。
- Soong。无法使用 Soong 构建系统构建
custom_images。 - OTA 更新。自定义映像用作出厂 ROM 映像,无法用于 OTA 更新。
维护分区之间的 ABI
odm 分区是 vendor 分区的扩展。在考虑应用二进制接口 (ABI) 稳定性时,请记住以下架构。
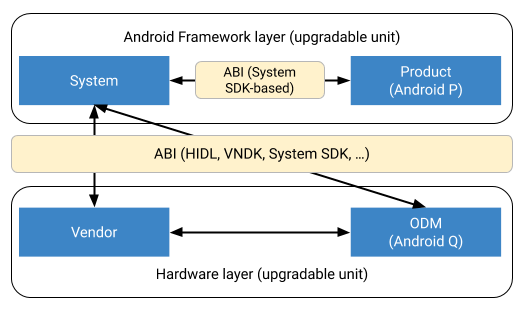
图 1. 维护分区之间的 ABI。
odm和vendor分区之间不具有 ABI 稳定性。必须同时升级这两个分区。odm和vendor分区可以相互依赖,但是在没有odm分区的情况下,vendor分区必须正常运行。odm和system之间的 ABI 与vendor和system之间的 ABI 相同。
product 分区不得与 vendor 或 odm 分区有直接交互。(这一规则将由 SEpolicy 强制执行。)
实现 ODM 分区
在实现新分区之前,请先了解相关 AOSP 变化。
设置 ODM 分区
如需设置 odm 分区,请添加以下构建标志:
BOARD_ODMIMAGE_PARTITION_SIZE(适用于固定分区大小)PRODUCT_USE_DYNAMIC_PARTITIONS和BOARD_ODMIMAGE_PARTITION_RESERVED_SIZE(适用于动态分区大小)BOARD_ODMIMAGE_FILE_SYSTEM_TYPE文件系统类型(用于 ODM 映像)/odm/build.prop的PRODUCT_ODM_PROPERTIES(在$(call inherit-product path/to/device.mk)内使用,如在PRODUCT_ODM_PROPERTIES += product.abc=ok中一样)
向 ODM 分区中安装模块
可使用以下构建标志向 odm 分区中安装模块:
device_specific: true(在Android.bp中)LOCAL_ODM_MODULE := true(在Android.mk中)
启用启动时验证
为防止恶意软件篡改 odm 分区,可为这些分区启用 Android 启动时验证 (AVB)(就像为 vendor 和 system 分区启用一样)。
如需启用 AVB,请添加构建标志 BOARD_AVB_ODM_ADD_HASHTREE_FOOTER_ARGS。如需详细了解如何在动态分区上配置 AVB,请参阅 AVB 配置更改。
将 /odm 作为另一个 /vendor 分区处理
如需确保系统将 odm 分区当作 vendor 分区处理,请将所有硬编码的 vendor 引用替换为一组面向硬件的分区(当前为 odm 和 vendor)。平台中值得注意的 vendor 引用位置包括动态链接器、软件包管理器和 shell/libc。
