本文详细介绍了 3.5 毫米插头耳机和 USB 耳机的功能要求。
在验证设备和音频耳机的行为时,请注意以下要求:
- 仅在没有其他可用音频配件(如蓝牙)时适用
- 涵盖设备的默认行为,不适用于使用音频导向 API 来选择要使用的音频外设的应用
媒体
如果用户在播放媒体时将耳机连接到设备,则只能通过耳机听到音频输出(声音)。
例如,当使用开源通用音乐播放器播放媒体时,按播放/暂停按钮应暂停播放。在媒体暂停时按同一按钮应继续播放。
如果耳机具有音量控制按钮:
- 每次按下音量调高按钮都应逐渐调高音量,直到达到最大音量。如果一直按住音量调高按钮,音量应逐渐增加到最大音量设置。
- 每次按下音量调低按钮都应逐渐调低音量,直到完全静音。如果一直按住音量调低按钮,音量应逐渐降低至静音。
- 在静音状态下按下音量调高按钮,应从静音开始一次增加一个等级的音量。
针对应用的建议:断开耳机连接时,声音输出应停止,且播放应暂停。在重新连接时,播放不应再次开始,除非用户按下播放按钮。按下播放时,应再次限于通过耳机输出声音。
一个按钮
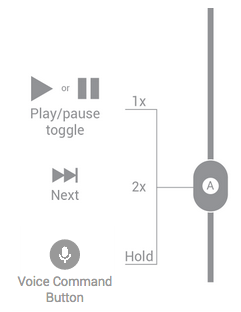
图 1. 单按钮耳机处理媒体流的按钮功能。
两个按钮
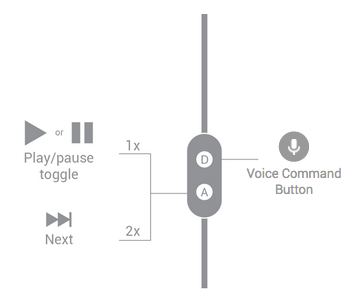
图 2. 双按钮耳机处理媒体流的按钮功能。
三个按钮
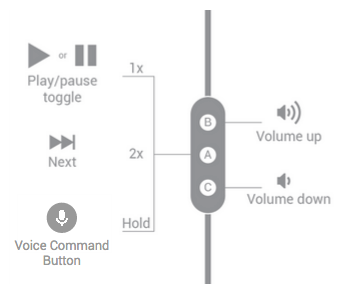
图 3. 三按钮耳机处理媒体流的按钮功能。
四个按钮
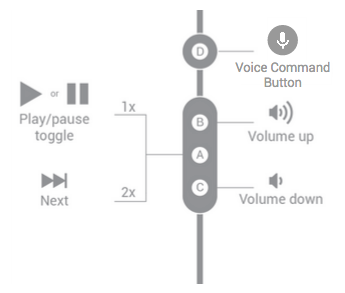
图 4. 四按钮耳机处理媒体流的按钮功能。
电话
如果用户在通话过程中将耳机连接到设备,则应在耳机上继续通话。通话不应被打断,且麦克风不应静音。音量按钮(如果存在)的行为应与媒体播放完全相同。
注意:静音和挂断电话的操作可能会因 Android 设备而异。本文描述的是最常见的行为;但对于某些设备,短按耳机按钮会使通话静音,而长按会挂断电话。
一个按钮
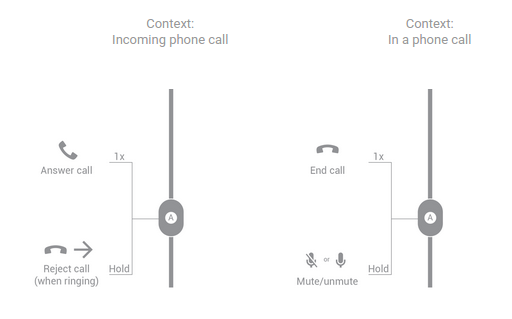
图 5. 单按钮耳机处理通话的按钮功能。
两个按钮
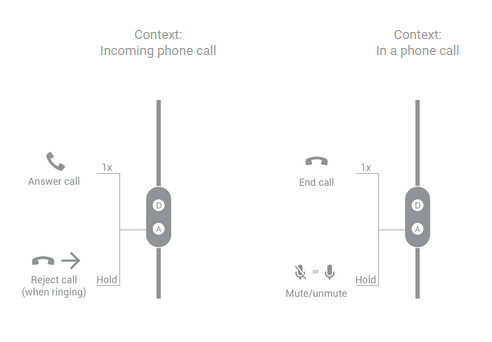
图 6. 双按钮耳机处理通话的按钮功能。
三个按钮
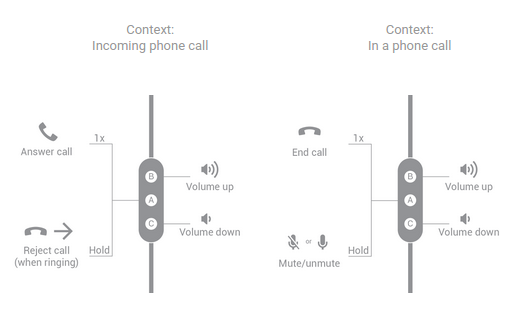
图 7. 三按钮耳机处理通话的按钮功能。
四个按钮
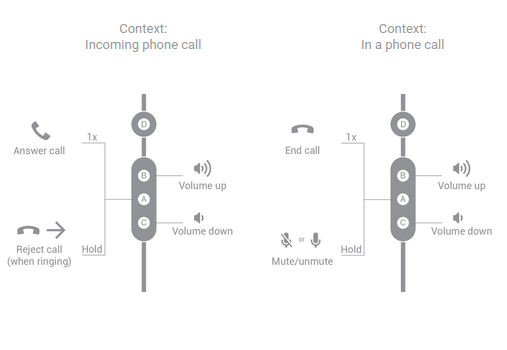
图 8. 四按钮耳机处理通话的按钮功能。
语音指令
语音指令按钮是一种新的内嵌控制标准,用于从任何已获批的穿戴式音频设备一致且方便地访问语音指令功能。通过按下此处定义的按钮,用户将听到双音信号耳标,表示设备正在聆听并准备好接收查询。
无论是内嵌到多功能按钮中还是单独采用单个按钮,都应可快速访问,符合人体工程学,并按照以下部分所述放置在显著位置。
按钮和功能映射建议
下图描述了 Android 语音指令按钮的可接受配置。
选项
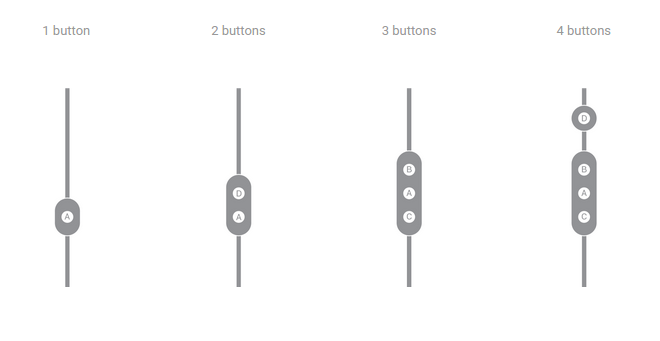
图 9. 按钮配置选项。
按钮应始终朝向前方且隔开,以便只通过触摸便可轻松找到它们。
间距
按钮直径必须大于 5 毫米,并且按钮之间的距离必须至少为 5 毫米。对于四按钮耳机,按钮 D 与其他按钮集群之间必须至少有 9 毫米的间隔。
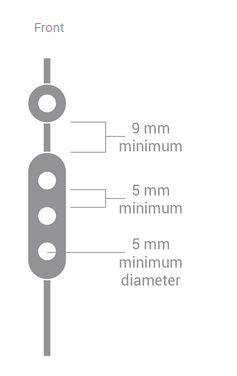
图 10. 按钮间距要求。
图标
在下图中,A 未标记或用圆点进行标记。B 用 + 或向上箭头进行标记。C 用 - 或向下箭头进行标记。D 用选定的按钮图标进行标记。
图 11. 按钮图标要求。
大小
下图显示了按钮图标与其周围空间的比例。
图 12. 语音搜索按钮图标大小要求。
麦克风端口
在操作按钮时,麦克风绝不应被遮挡。将端口放在远离手指操作区域的位置。
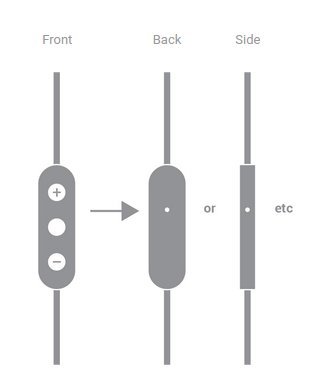
图 13. 麦克风位置。
