Android 9 支持根据运行供应商测试套件 (VTS) 测试的设备来获取指定 HAL 实例的服务名称。通过运行可感知服务名称的 VST HAL 测试,开发者能够实现在运行 VTS 测试的目标端和主机端自动测试供应商扩展程序、多个 HAL 以及多个 HAL 实例。
关于服务名称
每个运行中的 HAL 服务实例都会使用服务名称对自身进行注册。
在以前的 Android 版本中,运行 VTS HAL 测试的开发者必须在 getService() 中为测试客户端设置正确的服务名称,或将此名称留空并回退到默认的服务名称。这种方法的缺点包括:
- 依赖测试开发者的知识来设置正确的服务名称。
- 默认情况下,仅限于针对单个服务实例进行测试。
- 手动维护服务名称(即:由于名称是硬编码的,因此如果服务名称发生更改,则必须手动更新)。
在 Android 9 中,开发者可以根据所测试的设备自动获取指定 HAL 实例的服务名称。这种方法的好处包括支持测试以下各项:
- 供应商 HAL 扩展程序:例如,当供应商实现在供应商设备上运行的 camera.provider HAL 并针对此实现采用自定义服务名称时,VTS 可以识别此供应商实例并对其运行测试。
- 多个 HAL 实例:例如,当
graphics.composerHAL 拥有两个实例(一个采用服务名称"default",另一个采用服务名称“vr”)时,VTS 可以识别这两个实例,并分别对其运行测试。 - 多 HAL 测试:在测试拥有多个实例的多个 HAL 时使用。例如,在运行的 VTS 测试负责验证 keymaster 和 gatekeeper HAL 的协作情况时,VTS 可以测试这些 HAL 的服务实例的所有组合。
目标端测试
为了能够在进行目标端测试时感知服务名称,Android 9 添加了一种可自定义的测试环境 (VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase),该环境提供执行以下操作的接口:
- 在测试中注册目标 HAL。
- 列出所有已注册的 HAL。
- 获取 VTS 框架提供的已注册 HAL 的服务名称。
此外,VTS 框架还针对以下操作提供运行时支持:
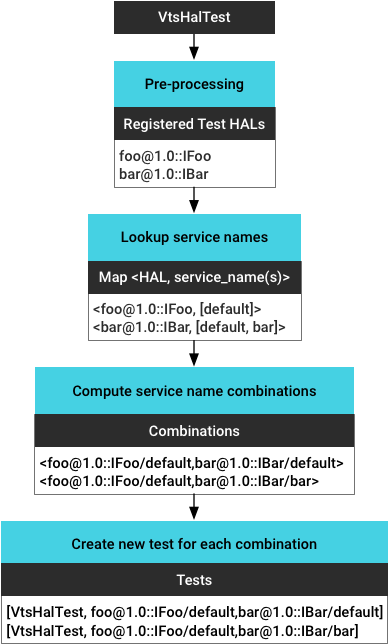
- 预处理测试二进制文件,以获取所有已注册的测试 HAL。
- 识别所有运行中的服务实例,并获取每个实例的服务名称(根据
vendor/manifest.xml进行检索)。 - 计算所有实例组合(以支持多 HAL 测试)。
- 针对每个服务实例(组合)生成新测试。
示例:
设置可感知服务名称的目标端测试
如需设置测试环境以便进行可感知服务名称的目标端测试,请执行以下操作:
- 根据
VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase定义testEnvironment,然后注册测试 HAL:#include <VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase.h> class testEnvironment : public::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase { virtual void registerTestServices() override { registerTestService<IFoo>(); } };
- 使用测试环境提供的
getServiceName()来传递服务名称:::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestBase::getService<IFoo>(testEnv->getServiceName<IFoo>("default")); // "default" is the default service name you want to use.
- 在
main()和initTest中注册测试环境:int main(int argc, char** argv) { testEnv = new testEnvironment(); ::testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(testEnv); ::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); testEnv->init(argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); }
如需查看其他示例,请参阅 VtsHalCameraProviderV2_4TargetTest.cpp。
VTS 主机端测试
VTS 主机端测试会在主机端上运行测试脚本,而不是在目标设备上运行测试二进制文件。如需为这些测试启用服务名称感知功能,您可以使用主机端模板针对不同参数多次运行同一测试脚本(类似于 gtest 参数化测试)。

- HAL 测试脚本负责在测试中指定目标 HAL 服务。
-
hal_hidl_host_test(param_test的子类)负责从测试脚本中提取已注册的测试 HAL,识别测试 HAL 对应的服务名称,然后生成服务名称组合(如果是多 HAL 测试)作为测试参数。此外,它还会提供getHalServiceName()方法,以便根据传递给当前测试用例的参数返回对应的服务名称。 - param_test 模板负责协助逻辑接受参数列表并针对每个参数运行所有指定的测试用例。也就是说,它会针对每个测试用例分别生成 N 个新的参数化测试用例(N = 参数大小),并且每个用例都具有一个指定的参数。
设置可感知服务名称的主机端测试
如需设置测试环境以便进行可感知服务名称的主机端测试,请执行以下操作:
- 在测试脚本中指定目标 HAL 服务:
TEST_HAL_SERVICES = { "android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo" }
- 调用
getHalServiceName()并将相应名称传递给 init hal:self.dut.hal.InitHidlHal( target_type='foo', target_basepaths=self.dut.libPaths, target_version=1.0, target_package='android.hardware.foo', target_component_name='IFoo', hw_binder_service_name =self.getHalServiceName("android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo"), bits=int(self.abi_bitness))
如需查看其他示例,请参阅 VtsHalMediaOmxStoreV1_0HostTest.py。
注册测试 HAL
在之前的 Android 版本中,VTS 利用在 AndroidTest.xml 中配置的 <precondition-lshal> 选项来识别测试 HAL。这种方法不仅难以维护(因为这种方法依赖开发者正确配置测试并相应地更新配置),而且不准确(因为这种方法仅包含软件包和版本信息,而不包含接口信息)。
在 Android 9 中,VTS 利用服务名称感知功能来识别测试 HAL。已注册的测试 HAL 还可用于以下操作:
- 前提条件检查:在运行 HAL 测试之前,VTS 可以确认目标设备上是否具有测试 HAL,并在没有时跳过相应测试(请参阅 VTS 可测试性检查)。
- 覆盖率衡量:VTS 可以获悉要衡量的测试 HAL 服务的相关信息,从而协助进行跨进程的代码覆盖率衡量(即刷新 HAL 服务进程的覆盖率)。
