为了在供应商与系统之间实现关注点分离,供应商原生开发套件 (VNDK) 需要对代码库进行一些更改。请按照以下指南在供应商/OEM 代码库中启用 VNDK。
构建系统库
构建系统包含多种类型的对象,其中包括库(共享、静态或头文件)和二进制文件。
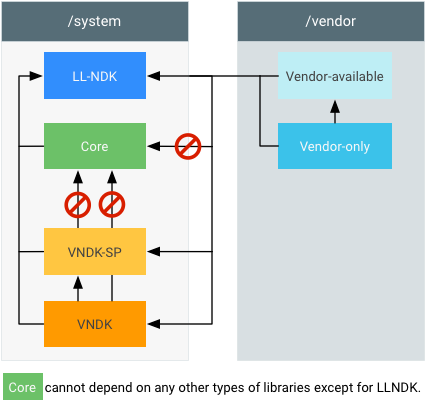
图 1. 编译系统库。
core库位于系统映像中,由系统映像使用。此类库不能由vendor、vendor_available、vndk或vndk-sp库使用。cc_library { name: "libThatIsCore", ... }
vendor-only(或proprietary)库位于供应商映像中,由供应商映像使用。cc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorOnly", proprietary: true, # or: vendor: true, # (for things in AOSP) ... }
vendor_available库位于供应商映像中,由供应商映像使用(可能包含core的副本)。cc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorAvailable", vendor_available: true, ... }
vndk库位于系统映像中,由供应商映像使用。cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndk", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, } ... }
vndk-sp库由供应商映像使用,同时也由系统映像间接使用。cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndkSp", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, support_system_process: true, } ... }
llndk库同时由系统映像和供应商映像使用。cc_library { name: "libThatIsLlndk", llndk: { symbol_file: "libthatisllndk.map.txt" } ... }
当库标记为 vendor_available:true 时,它将构建两次:
- 一次是为平台构建(因此被安装到
/system/lib中) - 一次是为供应商构建(因此被安装到
/vendor/lib或 VNDK APEX 中)
库的供应商版本使用 -D__ANDROID_VNDK__ 标记构建。您可以使用此标记停用在 Android 未来版本中可能会发生显著变化的专用系统组件。此外,不同的库会导出一组不同的头文件(如 liblog)。您可以在 Android.bp 文件中指定目标的供应商变体特有的选项:
target: { vendor: { … } }为代码库启用 VNDK
要为代码库启用 VNDK,请执行以下操作:
- 通过计算
vendor.img和system.img分区的所需大小来确定是否符合条件。 - 启用
BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current。您可以将其添加到BoardConfig.mk,也可以直接使用它来构建组件(例如m -j BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current MY-LIB)。
启用 BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current 后,构建系统会强行实施以下依赖项和头文件要求。
管理依赖项
如果 vendor 对象依赖的 core 组件在 vndk 中不存在或未以 vendor 对象的形式存在,必须通过以下某种方式解决该问题:
- 可以移除该依赖项。
- 如果该
core组件归vendor所有,可以将其标记为vendor_available或vendor。 - 可以在上游向 Google 提交更改请求,以便将此核心对象列入
vndk。
此外,如果有 core 组件依赖于 vendor 组件,就必须使该 vendor 组件成为 core 组件,或者以其他方式移除这种依赖关系(例如,通过移除该依赖项或将其移到 vendor 组件中)。
管理头文件
必须移除全局头文件依赖项,构建系统才能知道在构建头文件时是否带 -D__ANDROID_VNDK__。例如,您仍然可以使用头文件库 libutils_headers 访问 utils/StrongPointer.h 等 libutils 头文件。
某些头文件(例如 unistd.h)不能再以传递方式包含,但可以在本地包含。
最后,private/android_filesystem_config.h 的公共部分已移至 cutils/android_filesystem_config.h。如需管理这些头文件,请执行下列操作之一:
- 通过将所有
AID_*宏替换为getgrnam/getpwnam调用(如果可能),移除对private/android_filesystem_config.h的依赖。例如:(uid_t)AID_WIFI变为getpwnam("wifi")->pw_uid。(gid_t)AID_SDCARD_R变为getgrnam("sdcard_r")->gr_gid。
private/android_filesystem_config.h。 - 对于硬编码的 AIS,请包含
cutils/android_filesystem_config.h。
