从 Android 15 开始,自适应刷新率 (ARR) 功能可让显示屏刷新率使用离散的 VSync 步长来适应内容帧速率。
ARR 功能具有以下优势:
降低功耗:默认情况下,ARR 可让设备以低于其最大刷新率的刷新率运行,仅在刷新率对用户体验至关重要时才转换为更高的刷新率,从而最大限度地减少不必要的功耗。
减少卡顿:使用 ARR 时,将不再需要切换模式,而切换模式是导致卡顿的已知原因之一。
概览
在非 ARR 面板上,显示屏会按照由有效显示模式确定的固定频率进行刷新。
在 ARR 面板上,显示屏的 VSync 速率和刷新率已解耦,这使得刷新率在一种显示模式下可随内容更新频率而改变。面板的刷新率可以是面板撕裂效应 (TE) 频率的整数倍。OEM 可以根据首选的功耗权衡方式来灵活实现 ARR。
在下图中,显示屏的 vsyncPeriod 为 240 Hz,minFrameIntervalNs(最大刷新率)为 120 Hz。VSync 每 4.16 毫秒发生一次。帧能够以最后一帧的 minFrameIntervalNs 之后的 VSync 的任意倍数呈现。
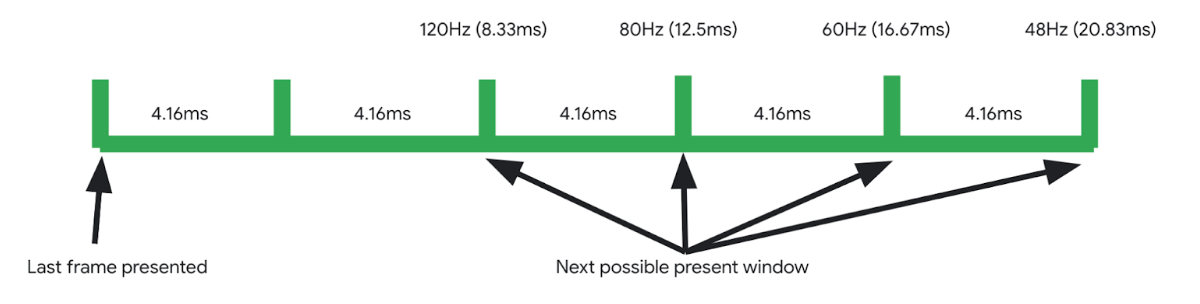
图 1. ARR 示例。
实现
得益于新增的 Hardware Composer (HWC) HAL API 和平台更改,Android 15 现在支持 ARR。如需启用 ARR,OEM 必须支持搭载 Android 15 及更高版本的设备上的内核和系统更改,并实现 android.hardware.graphics.composer3 API 3,如以下各个部分所列。
如需了解详情,请参阅支持 ARR 的 API 对应的 Pixel 的参考实现。
DisplayConfiguration.aidl
DisplayConfiguration.aidl API 使用显示属性以及 ARR 的以下属性指定显示配置:
- 可选的
vrrConfig:如果设置了此参数,系统会为特定配置启用 ARR。如果设置为null,显示模式会设置为非 ARR 模式,例如多刷新率 (MRR)。借助此属性,可以将显示屏配置为 MRR 或 ARR,但不能同时配置为这两者。 vsyncPeriod:显示屏的 VSync 速率。在 ARR 显示屏上,此值用于得出支持的离散刷新率。供应商必须为所有设备设置
DisplayConfiguration.vsyncPeriod值。对于非 ARR 显示屏,DisplayConfiguration.vsyncPeriod是显示屏刷新率。如果设备支持 120 Hz,则此值必须为 8.3 毫秒。对于 ARR 显示屏,
DisplayConfiguration.vsyncPeriod是 TE 信号频率。如果设备的minFrameIntervalNs为 8.3 毫秒,但 TE 为 240 赫兹,则此值必须为 4.16 毫秒。
VrrConfig.aidl
VrrConfig.aidl API 包含以下属性:
minFrameIntervalNs:显示屏可支持的最大刷新率。NotifyExpectedPresentConfig:这取决于显示屏何时需要提前通知即将呈现的帧。
IComposerClient.notifyExpectedPresent 会为可能呈现的帧提供提示,以便显示屏可以相应地调整其自刷新周期。frameIntervalNs 表示 expectedPresentTime 之后的呈现节奏。例如,如果调用 notifyExpectedPresent,且 expectedPresentTime 为 N,frameIntervalNs 为 16.6 毫秒,那么下一帧的呈现时间为 N + 16.6 毫秒。在呈现时间 N 处,帧频率为 16.6 毫秒,直到发生进一步更改。
只有在设置了 DisplayConfiguration.notifyExpectedPresentConfig 且发生以下某个时间条件时,系统才会调用 IComposerClient.notifyExpectedPresent:
- 不合节奏的呈现时间:下一帧的预期呈现时间偏离了由
frameIntervalNs定义的显示屏常规刷新率。 - 超时:前一帧与当前帧之间的时间间隔大于或等于
notifyExpectedPresentConfig.timeoutNs。
DisplayCommand.frameIntervalNs
DisplayCommand.frameIntervalNs 以纳秒为单位针对即将呈现的帧提供节奏提示。
测试
使用 onRefreshRateChangedDebug 进行调试。此方法会通知客户端,让其知道显示屏的刷新率已更改。
使用 TouchLatency 测试应用进行手动测试,如图 2 所示:
图 2. TouchLatency 测试应用。
在该测试应用中,可以使用滑块将呈现速率调整为显示屏刷新率的各种整倍数刷新率。观察帧速率如何随请求的速率而变化。
