For devices running Android 13 or higher, Android supports the Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) standard. This page describes Android Wi-Fi 7 features, including baseline and multi-link operation (MLO).
Baseline Wi-Fi 7 features
This section describes baseline Wi-Fi 7 features included in Android 13 and higher.
Device Wi-Fi 7 support
The Android framework includes the
WifiManager#isWifiStandardSupported(int standard)
API, which apps can call with the
ScanResults.WIFI_STANDARD_11BE
argument, to check whether a device supports Wi-Fi 7.
When this API is called, the
Wi-Fi module
checks whether the config_wifi11beSupportOverride configuration overlay is
used as an override and does the following:
- If the overlay is set to
true, the device is assumed to support Wi-Fi 7 regardless of the response from nl80211. This override is useful only for device manufacturers that don't have drivers that return support of Wi-Fi 7. - If the overlay is set to
false(default value), the Wi-Fi module uses the information from nl80211. The Wi-Fi module requests the information from wificond, which calls the nl80211 commandNL80211_CMD_GET_WIPHY. If theNL80211_BAND_IFTYPE_ATTR_EHT_CAP_PHYattribute is in the response from the driver, the device is assumed to support Wi-Fi 7.
Scanned AP Wi-Fi 7 support
The Android framework includes the
int ScanResult#getWifiStandard()
API, which apps can call to check whether a scanned access point (AP)
supports Wi-Fi 7. If the AP supports Wi-FI 7, the API returns
ScanResults.WIFI_STANDARD_11BE.
The device isn't required to support Wi-Fi 7 for apps to use this API.
When this API is called, the Wi-Fi module checks whether EHT Capability IE is
in the returned results of the connectivity scan. If EHT Capability IE is in
the scan results, the scanned AP supports Wi-Fi 7.
The AOSP WifiTracker class displays this support information in the user
interface when running in verbose mode.
STA connection mode
The Android framework includes the
int WifiInfo#getWifiStandard()
API, which apps can call to check whether the current station (STA) connection
mode is Wi-Fi 7. The STA connection mode is Wi-Fi 7 when both the device and
the connected AP support Wi-Fi 7. If the connection mode is Wi-Fi 7, the API
returns
ScanResults.WIFI_STANDARD_11BE.
When the getWifiStandard is called, the Wi-Fi module determines the mode by
calling the
ISupplicantStaIface#getConnectionCapabilities() HAL API. The
implementation of this HAL API in the wpa_supplicant AIDL layer checks whether
EHT Capability IE is in both AssocReq and AssocRsp during the
connection setup.
Network selection
In Android 13, network selection uses several
parameters to determine which AP to connect to. One of the parameters is the
estimated throughput of the AP, which is estimated using the
ThroughputPredictor block. The
ThroughputPredictor block uses the PHY parameters of both the device and the
scanned AP.
In Android 13, ThroughputPredictor uses the
following AP capabilities in its calculation:
- Support of Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be)
- Support of 320 MHz channel width
Including these capabilities in ThroughputPredictor logic boosts the
chances for selecting Wi-Fi 7 capable APs when the device can make use of these
features.
Wi-Fi RTT-based ranging
Android provides API support for EHT preamble and 320 MHz channel width for Wi-Fi RTT. This enables the support of Wi-Fi 7 related capabilities in RTT ranging whenever it's supported by the chip.
HAL APIs
The following HAL APIs support the Wi-Fi 7 capabilities for RTT-based ranging:
EHT: Constant inenum RttPreambleandenum WifiRatePreambleWIDTH_320: Constant inenum WifiChannelWidthInMhzBW_320MHz: Constant inenum RttBw
APIs
Apps can use the following APIs for Wi-Fi 7 RTT-based ranging:
ScanResult#PREAMBLE_EHTResponderConfig#PREAMBLE_EHT(SystemApi)
Soft AP
Android supports Wi-Fi 7 in Soft AP and provides the following features.
Start Soft AP
Android supports starting Soft AP in Wi-Fi 7 mode.
This is governed by the config_wifiSoftapIeee80211beSupported overlay
configuration.
The Wi-Fi module uses the overlay config_wifiSoftapIeee80211beSupported to set
the boolean HwModeParams#enable80211BE in the
IHostApd#addAccessPoint() API call. In the hostapd AIDL layer, this value is
used to set the hostapd.conf parameters.
HAL APIs
The
enable80211BE
boolean in HwModeParams in the hostapd HAL supports
starting Soft AP in Wi-Fi 7 mode.
Report Soft AP information
Android includes API support to include Wi-Fi 7 and 320 MHz channel width information in the reported Soft AP information.
HAL APIs
The WIFI_STANDARD_11BE constant in the
Generation.aidl
AIDL interface in the hostapd HAL, which is used
in the ApInfo reported in the IHostapdCallback#onApInstanceInfoChanged()
callback, supports reporting Soft AP information.
APIs
Apps can use the following methods (system APIs) in
SoftApInfo
to report Soft AP information.
SoftApInfo#getWifiStandard(): ReturnsScanResults.WIFI_STANDARD_11BEif the Soft AP is started in Wi-Fi 7 mode.SoftApInfo#getBandwidth(): ReturnsSoftApInfo#CHANNEL_WIDTH_320MHZif the 320 MHz channel width is used.
MLO Wi-Fi 7 features
Multi-link operation (MLO) is the main feature in the Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) specification. MLO is a mandatory feature for multi-link devices (MLD) running in Wi-Fi 7, whether concurrently or nonconcurrently.

Figure 1. MLO diagram.
As shown in Figure 1, both the AP-MLD and STA-MLD have multiple AP or STA instances running on each link. Each link has a separate AP or STA MAC address. The AP or STA also has an MLD MAC address to identify the device.
MLO link representation
The
android.net.wifi.MloLink
class represents the MLO link. This class includes the following parameters:
int getLinkId(): Link ID as advertised by the AP MLD.MacAddress getApMacAddress(): AP MAC address. The BSSID of the AP instance for that link.MacAddress getStaMacAddress(): STA MAC address. The locally assigned MAC address for the STA instance on the link.int getChannel(): Link channel. The channel number of the link.int getBand(): Link band. The band of the link.int getState(): Link state. Can be one of the following states:MLO_LINK_STATE_INVALID: Invalid. Used for initialization and error cases.MLO_LINK_STATE_UNASSOCIATED: Unassociated. The link isn't associated with an AP.MLO_LINK_STATE_IDLE: Idle. The link is associated but not active (no traffic identifier (TID) is mapped to the link).MLO_LINK_STATE_ACTIVE: Active. The link is associated and active (at least one TID is mapped to the link). An active link can be in power save mode because the framework doesn't monitor the power state of the link.
Scanned Wi-Fi 7 AP MLO information
Apps can get the MLO parameters for a Wi-Fi 7 AP MLD when the Wi-Fi module
receives a
ScanResult
object from the AP-MLD. The AOSP WifiTracker displays the MLO parameters when
running in verbose mode.
The Wi-Fi module collects the MLO information by doing the following:
- Parses the multi-link information element (IE) included in the beacon or probe response to read the AP MLD MAC address and the current link ID.
- Parses the reduced neighbor report (RNR) IE included in the beacon or probe response to read the list of the affiliated links information.
APIs
To get scanned AP MLO information, apps can use the following APIs:
ScanResult#BSSID: The AP instance MAC address (for the link on which the scan result is received)MacAddress ScanResult#getApMldMacAddress(): Returns the MLD MAC address of the AP.int ScanResult#getApMloLinkId(): Returns the link ID for the link on which the ScanResult was received.List<MloLink> ScanResult#getAffiliatedMloLinks(): Returns a list ofMloLinkobjects for all the links advertised by the AP-MLD including the link on which the ScanResult was received.
Connected Wi-Fi 7 AP MLO information
When a device connects to a Wi-Fi 7 AP-MLD, the framework collects the
MLO parameters of the connection from the WifiInfo object. The AOSP
WifiTracker object displays this information when running in verbose mode.
When the device connects with the AP-MLD, the Wi-Fi module copies the MLO
information from the ScanResult object received from the AP. The module then
calls the ISupplicantStaIface#getConnectionMloLinksInfo() HAL API
to read the MAC addresses of each link for both AP and STA, and to update
the state of the associated links.
APIs
To get MLO connection information, apps can use the following APIs:
WifiInfo#getBSSID(): Returns the AP instance MAC address (for the link on which the device is associated).MacAddress WifiInfo#getApMldMacAddress(): Returns the MLD MAC address of the AP.int WifiInfo#getApMloLinkId(): Returns the link ID for the link on which the STA has associated with the AP.List<MloLink> WifiInfo#getAffiliatedMloLinks(): Returns a list ofMloLinkobjects for all the links advertised by the AP-MLD including the associated link. Both the AP and STA MAC addresses can be queried on eachMloLinkobject.
AP-MLD scanning
The vendor software provides the Wi-Fi framework with the scan results for each beacon or probe response it receives. This means that the Wi-Fi framework:
- Might receive multiple
ScanResultsobjects from the same AP-MLD because the AP can have multiple beaconing links. - Might receive only a partial set of the scan results for the AP links of an AP-MLD because some of these link signals might not be received by the firmware.
The vendor software reports only scan results received over the air, and must not create (artificially synthesize) scan results based on advertised links by the AP-MLD.
The vendor software must include the basic variant multi-link and RNR IEs received from the AP instances in the reported scan results. If affiliated AP details are missing in the scan results, the vendor software can send multi-link probe requests (probe request frame that includes a probe Request multi-link element) to include the complete or partial set of capabilities, parameters, and operation elements of the AP with the targeted AP-MLD in the response frame.
The vendor software can trigger ML-probing (using probe req variant ML IE in the probe req frame) if required.
AP-MLD network association
When a device joins an AP-MLD network, the vendor software uses the selected AP link (associated link) for signaling. The vendor software can associate to all or some of the links that are supported by the device.
Upon successful association, the driver reports
ISupplicantStaIfaceCallback#onStateChanged() with the BSSID of a link for
the AP-MLD. The driver then selects a link of the AP-MLD provided that
scan results were reported to the framework for that link.
Network scoring
For devices running Android 14 or higher, Android Wi-Fi Network Selection supports Wi-Fi 7 MLO. This means Android selects the best Wi-Fi network for the device based on the number of links available for MLO.
To support MLO, the network selection algorithm uses the following MLO capabilities from the Wi-Fi chip:
- Maximum STR link count
- Maximum association link count
- Simultaneous band combinations
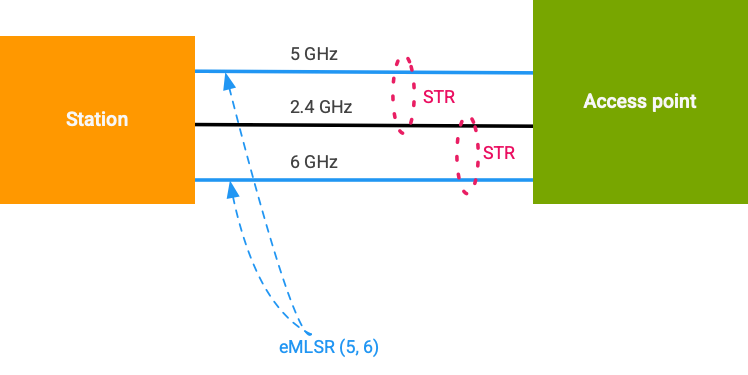
Figure 2. MLO network selection.
Maximum STR link count
Simultaneous transmit and receive (STR) is a Wi-Fi medium contention scheme for multi-link operation. The signal isolation between different links is sufficient so that the links can operate independently and are capable of transmitting and receiving simultaneously in different links. STR is different from legacy single link (SL) STA and legacy dual band dual concurrent (DBDC) STA. STAs affiliated with a STA MLD share a common transmitter sequence number (SN) and a common space for data transmission allocated to different links if multiple links transmission have the same access category (AC).
The maximum number of STR links used can be different from the maximum number of radios supported by the chip. In the example in Figure 2, the maximum STR link count is 2.
The following AIDL HAL interfaces support the maximum STR link count and maximum number of association link count capabilities:
hardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/IWifiChip.aidlhardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/WifiChipCapabilities.aidl
Maximum association link count
Multiple links can operate on a single radio using the contention scheme, Enhanced Multi-Link Single Radio (eMLSR). A multi-link device uses eMLSR over a set of links if it can receive certain basic control frames and perform clear channel assessment (CCA) simultaneously on the set of links. However, the MLD transmits or receives data on only one link (the link chosen dynamically in each transmit opportunity (TXOP) period) at a time.
A MLD station can maximize the number of association links for better reliability, better throughput, and lower latency (as compared to a single link legacy station) by concurrently operating in STR and eMLSR if supported by the chip. In Figure 2, the maximum association link count is 3.
The following AIDL HAL interfaces support the maximum association link count capability:
hardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/IWifiChip.aidlhardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/WifiChipCapabilities.aidl
Simultaneous band combinations
The framework queries the chip to get the allowed radio combinations (through
the IWifiChip.aidl AIDL interface) that can operate simultaneously. From this
information, the framework derives possible simultaneous band combinations. The
following is an example list of simultaneous band combinations (GHz):
- 2.4
- 5
- 6
- 2.4 x 5
- 2.4 x 6
- 5 x 6
The following AIDL HAL interface supports simultaneous radio combinations:
hardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/IWifiChip.aidl
Network selection
During network selection (MLO), the candidate list is grouped by members with the same MLD MAC address. The maximum predicted multi-link throughput score is calculated for each group, based on the maximum STR link count and simultaneous band combinations supported by the chip. If the candidate is multi-link capable and the chip supports STR, the predicted throughput score is replaced with the multi-link predicated throughput score. This gives a boost to MLO candidates during network selection.
When joining an AP-MLD network, the framework performs the SSID selection based
on information received in the ScanResults object as reported by the vendor
software. Upon SSID selection by the framework, the vendor software is
responsible for selecting the BSSID for the best AP (or AP link) to use for
association.
Device STA MAC address handling
This section describes how device STA MAC addresses (MLD MAC addresses and per-link STA MAC addresses) are handled.
MLD MAC address
The Wi-Fi framework manages the MLD MAC address of the device. The MLD MAC
address is handled the same way a non-MLD device handles its own MAC address.
The MAC address can be a randomized MAC address or a hardware provisioned MAC
address based on the user's choice. The MLD MAC address is set by the framework
using the IWifiStaIface#setMacAddress() HAL API.
Per-Link STA MAC address
The vendor software manages instance STA MAC addresses (for each link). When a device associates with an AP, the vendor software assigns an instance MAC address for each associated link.
The vendor software assigns per-link MAC addresses based on its algorithm. The algorithm must be repeatable and be a function of the following:
- STA-MLD MAC address set by the Wi-Fi framework.
- Link ID (received from AP)
This means that if the framework reuses the same MLD MAC address, the vendor must reuse the same associated per-instance MAC addresses, and if the vendor reuses the per-instance MAC addresses, the framework must reuse the same MLD MAC address. This verifies that when the framework-generated STA-MLD address is persistent for an SSID, the per-STA MAC addresses are also persistent.
The following is an example algorithm for per-link STA MAC address assignment (vendors can implement any algorithm that meets the algorithm criteria):
- Octet 0: Make sure the locally administered bit is set
- Octet 1-4: Same as STA-MLD MAC Address
- Octet 5: Per-STA = (STA-MLD + link ID + 1) MOD (256)
Multi-link handling
The vendor firmware can perform link switching and manage the power save state of the links for activation or deactivation without input from the Wi-Fi framework.
The Wi-Fi framework doesn't expect a notification when the link state is changed.
Management of power save state
Power save state is enabled by default on the Wi-Fi framework. In the power save state, the vendor firmware manages the power save state of individual links based on traffic patterns and link activation or deactivation decisions.
However, the Wi-Fi framework can force the power save state to be disabled by
calling the ISupplicantStaIface::setPowerSave(false) HAL API. If the
power save state is disabled by the framework, the vendor firmware must keep at
least one link active (power save disabled). In this state, the firmware
implementation decides which link is set.
Data path
This describes the vendor firmware implementation for handling uplink and download traffic.
Uplink traffic
The firmware routes uplink traffic to one (or more) links based on its internal implementation. The vendor firmware decides when to do load balancing, duplication, or aggregation of traffic based on traffic patterns. We recommend the firmware duplicate traffic to multiple links in the following cases:
- When low-latency mode is set through the
IWifiChip#setLatencyMode()HAL API. - When there is traffic with user priority 6 and 7.
Downlink traffic
The firmware must replace the (destination) per-STA MAC address of the MAC header with the MLD-STA MAC and the (source) per-AP MAC address of the MAC header with the MLD-AP MAC address. The firmware must perform this MAC address substitution before passing through the APF filter because the APF filter commands have filters based on MLD MAC addresses. There is a single APF filter for all the links of an AP-MLD.
Concurrency
Concurrency scenarios, where a radio is used for a new interface, must have priority over dedicating multiple radios for links of the same interface. Concurrency scenarios must also take priority over MLO no matter which came first. Using multiple links for a single interface is opportunistic, meaning that multiple links are used only when:
- MLO is required based on firmware decision for load balancing, aggregation, or duplication.
- MLO is available, meaning a radio isn't required by another interface.
TID-to-link mapping
For devices running Android 14 or higher, when the Wi-Fi 7 AP announces a temporary disablement of one of the links through a TID-to-link mapping element transmitted in beacon, probe response, and association response frames, the Wi-Fi 7 station continues the connection with the AP using the remaining links that are set up, without performing another association.
For devices running Android 13 or lower, the Wi-Fi framework doesn't support receiving notifications for when the link state is changed due to TID-to-link mapping, even if the associated link isn't linked to a TID.
AIDL HAL
The Wi-Fi supplicant notifies the Wi-Fi framework of TID-to-link mapping changes through the following AIDL interfaces:
hardware/interfaces/wifi/supplicant/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/supplicant/ISupplicantStaIfaceCallback.aidlhardware/interfaces/wifi/supplicant/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/supplicant/ISupplicantStaIface.aidlhardware/interfaces/wifi/supplicant/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/supplicant/MloLinksInfo.aidl
APIs
Apps can get information about TID-to-link mapping changes by using the following APIs:
ConnectivityManager.NetworkCallback.onCapabilitiesChanged(): Network callback triggered by the framework when there's a TID-to-link mapping change.WifiInfo#getAssociatedMloLinks(): Returns the associated MLO links.MloLink#getState(): Returns the state of the link,MLO_LINK_STATE_ACTIVEorMLO_LINK_STATE_IDLE.
TID-to-link mapping negotiation capabilities
For devices running Android 14 or higher, the following APIs are available to get the TID-to-link map negotiation capabilities for the station and AP.
Chip capability
The following interfaces support the chip capability for TID-to-link mapping negotiation.
AIDL HAL
The AIDL interface for TID-to-link mapping negotiation is in FeatureSetMask
in hardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/IWifiChip.aidl. The
T2LM_NEGOTIATION = 1 << 8 capability indicates that the chip supports
TID-to-link mapping.
APIs
WifiManager.isTidToLinkMappingNegotiationSupported(): Returns the chip that supports TID-to-link mapping negotiation.
AP capability
The following interfaces support the AP capability for TID-to-link mapping negotiation.
AIDL HAL
The framework queries the AP capability from the supplicant together with the current connection capability.
apTidToLinkMapNegotiationSupported: Checks whether an AP supports the TID-to-link map negotiating capability.
APIs
WifiInfo.isApTidToLinkMappingNegotiationSupported(): Returns whether AP supports TID-to-link mapping negotiation.
Link layer stats
Link layer stats include Wi-Fi link-specific details such as RSSI, various TX and RX packet counters, and radio stats. The Wi-Fi framework periodically polls link layer stats and RSSI to select the best network or to evaluate the quality of the connected network. For devices running Android 14 or higher, link layer stats include multi-link support. To support Wi-Fi 7, Android supports MLO in both link layer stats and signal polling.
Link-specific statistics are found in the following link layer AIDL interfaces:
hardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/StaLinkLayerIfaceStats.aidlhardware/interfaces/wifi/aidl/android/hardware/wifi/StaLinkLayerLinkStats.aidl
The
android.net.wifi.WifiManager#addOnWifiUsabilityStatsListener()
system API listens to all link layer stats. The framework periodically invokes
this API to update Wi-Fi usability statistics.
The following link-specific APIs are available in
android.net.wifi.WifiUsabilityStatsEntry.
int getRssi(int linkId)
int getLinkState(int linkId)
int getRadioId(int linkId)
int getTxLinkSpeedMbps(int linkId)
long getTotalTxSuccess(int linkId)
long getTotalTxRetries(int linkId)
long getTotalTxBad(int linkId)
long getTotalRxSuccess(int linkId)
long getTotalBeaconRx(int linkId)
int getRxLinkSpeedMbps(int linkId)
int getTimeSliceDutyCycleInPercent(int linkId)
ContentionTimeStats getContentionTimeStats(int linkId, @WmeAccessCategory int ac)
List<RateStats> getRateStats(int linkId)
To query available link IDs, apps can call the
android.net.wifi.WifiUsabilityStatsEntry#getLinkIds()
method.
APIs in
android.net.wifi.WifiUsabilityStatsEntry
for single link (not MLO) return the aggregated stats for MLO connections. The
following is the aggregation criteria:
The following aggregated packet statistics use the sum of per-link stats:
public long getTotalTxSuccess() public long getTotalTxRetries() public long getTotalTxBad() public long getTotalRxSuccess() public int getRxLinkSpeedMbps()The following statistics use the data from the link with the highest RSSI:
public int getRssi() public int getLinkSpeedMbps() public long getTotalBeaconRx() public int getTimeSliceDutyCycleInPercent() public ContentionTimeStats getContentionTimeStats(@WmeAccessCategory int ac) public List<RateStats> getRateStats()
Link layer stats in Android 13
For devices running Android 13, link layer stats
don't take into account the
usage of multiple links for a single interface. To support MLO, vendor software
must apply the following aggregation logic when reporting LinkLayerStats
through the IWifi# getLinkLayerStats_1_6() HAL API. The best link is the
link with the highest RSSI.
StaLinkLayerStats.iface.beaconRx: Report the beacon count for the best link used for the interface.StaLinkLayerStats.iface.avgRssiMgmt: ReportavgRssiMgmtfor the best link used for the interface.StaLinkLayerStats.iface.wmeXxPktStats(Xx = Vo, Vi, Be,Bk): Report the aggregated packet stats (total) over the links of the interface.StaLinkLayerStats.iface.wmeXxContentionTimeStats(Xx = Vo, Vi, Be,Bk): Report the contention time stats for the best link used on the interface (lowest contention time stats).
MLO link reconfiguration
When one of the links of the Wi-Fi 7 access point is repurposed, the AP can announce the removal of the link through MLO link reconfiguration. Stations can sustain seamless connectivity with the AP without a reassociation on the remaining links.
The
onMloLinksInfoChanged
AIDL interface, located in the Wi-Fi supplicant at
ISupplicantStaIfaceCallback.aidl,
supports link reconfiguration (AP removal of the link).
When the Wi-Fi framework processes the removal of a link, the link state is set
to
MLO_LINK_STATE_UNASSOCIATED.
The framework then triggers
ConnectivityManager.NetworkCallback#onCapabilitiesChanged()
for a link state change.
The
WifiInfo#getAffiliatedMloLinks
method returns the affiliated MLO Links. The
MloLink#getState
method returns the state of the link. If the link is removed, the returned link
state is
MLO_LINK_STATE_UNASSOCIATED.
Chip MLO strategy
MLO allows devices to send and receive data on multiple Wi-Fi links at the same time, which can improve performance for apps that have specific requirements such as low latency, high bandwidth, and low power. Chip vendors can develop algorithms on how to use the available links.
Privileged apps can modify these algorithms using the
setMloMode
method in Wifimanager and set the
following modes:
MLO_MODE_DEFAULT = 0MLO_MODE_LOW_LATENCY = 1MLO_MODE_HIGH_THROUGHPUT = 2MLO_MODE_LOW_POWER = 3
The framework uses
setMloMode
in the IWifiChip AIDL interface
to set the MLO mode.
